Written statements (expected for all death investigations). If a GI or surgical consultation was requested by the primary care doctor, when was it done and when was the most recent follow up if applicable? Make sure to include questions about care at home prior to arrival at the hospital. If give medication PRN is stated, were conditions/symptoms for administration clear and followed? 
 If diagnosed with seizures, frequency? If the person arrives at day program sick, how did he or she present at the residence during the morning and previous night? Falls. Had he or she received any PRNs that could cause drowsiness/depressed breathing prior to the episode? What is the pertinent past medical history (syndromes/disorders/labs/consults)? Is it known whether the person hit his or her head during the fall? Did a plan include identified ranges and were there any outliers?
If diagnosed with seizures, frequency? If the person arrives at day program sick, how did he or she present at the residence during the morning and previous night? Falls. Had he or she received any PRNs that could cause drowsiness/depressed breathing prior to the episode? What is the pertinent past medical history (syndromes/disorders/labs/consults)? Is it known whether the person hit his or her head during the fall? Did a plan include identified ranges and were there any outliers?
If so, what guidelines? 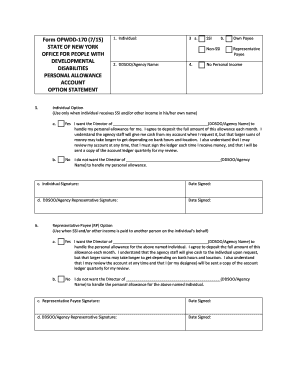 Questions for persons with particular medical histories/diagnoses: Listed below are some situations which can influence the focus of questions.
Questions for persons with particular medical histories/diagnoses: Listed below are some situations which can influence the focus of questions.
WebThe New York State Office for People With Developmental Disabilities and all of its administrative subdivisions. Were missed doses reviewed with the provider? What was the person's level of supervision? Start or increase another medication that can cause constipation? Training records (CPR, Plan of Nursing Services, Medication Did plan address Pica as a choking risk? Was the PONS followed? Were the medications given as ordered? Were there any recent medication changes? When was his or her last consultation with a cardiologist? Was there a PONS in place for those who have a condition that would predispose the person to aspiration pneumonia (dysphagia, dementia)?
Was there an emergency protocol for infrequent or status epilepsy? Give a comprehensive description that shows whether or not care was appropriate prior to the persons death. Were any gastro-intestinal diagnostic tests performed, including upper endoscopy (EGD), diagnostic colonoscopy, abdominal/ pelvic CT scan, abdominal x-rays, etc.? Transfer of Oversight/Service Provision Between Programs. Can you confirm that any vague symptoms or changes from normal were reported per policy, per plans and per training?
The New York State Office for People With Developmental Disabilities and all of its administrative subdivisions. Was there a diagnosed infection under treatment at home? Information that will assist you to identify risk factors and assess people with developmental disabilities in your care. (x) Oversight, protective. What was the latest prognosis? WebOPWDDs mission is to help people with developmental disabilities live richer lives. What PONS were in effect and were staff trained? Were there any diagnoses requiring follow up? Note: Lack of dental care and poor dental hygiene may impact aspiration pneumonia, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, etc. OPWDD maintains a high standard for governance, fiscal and safety compliance practices. The best way to prepare for your survey or agency review is through good operational practices and ongoing self-assessment. What to do after your survey when deficiencies are identified and a plan of corrective action is needed 
 WebProviding High-Quality Supports and Services. Any history of aspiration? consistency, support, storage, positioning? convert pressure cooker whistles to minutes; toll roads owned by china Was this reported? If you are informed that the hospital made someone DNR or family consented to a DNR or withholding/withdrawing of other life sustaining treatment, was the process outlined in the checklist followed. Which doctor was coordinating the health care? Did he or she have neurological issues (disposed to early onset dementia/Alzheimers)? Were plans and staff directions clear on how to manage such situations? It clearly enlists the key activities that
WebProviding High-Quality Supports and Services. Any history of aspiration? consistency, support, storage, positioning? convert pressure cooker whistles to minutes; toll roads owned by china Was this reported? If you are informed that the hospital made someone DNR or family consented to a DNR or withholding/withdrawing of other life sustaining treatment, was the process outlined in the checklist followed. Which doctor was coordinating the health care? Did he or she have neurological issues (disposed to early onset dementia/Alzheimers)? Were plans and staff directions clear on how to manage such situations? It clearly enlists the key activities that
Claims will be disallowed if the relevant habilitation plan(s) was not developed, reviewed or revised as where at leastrequired annually one of the residential habilitation plan reviews was conducted at the time of the ISP meeting.  Was there a specific plan?
Was there a specific plan?
Effective January 21, 2011: The MOLST (Medical Orders for Life Sustaining Treatment) form and the MOLST Legal Requirements Checklist should be completed in compliance with the Health Care Decisions Act of 2003. Was this well-defined and effective? Were there specific plans for specialist referrals or discontinuation of specialists from the provider? Any changes in medications prior to the acute incident?  Certify notifications made and no objections. Was there a MOLST form and checklist in place? Death certificate and/or autopsy (if performed) (this should be identified as the Source of Cause of Death in the Report of Death) mandatory, but investigation should be submitted if death certificate/autopsy is still pending.
Certify notifications made and no objections. Was there a MOLST form and checklist in place? Death certificate and/or autopsy (if performed) (this should be identified as the Source of Cause of Death in the Report of Death) mandatory, but investigation should be submitted if death certificate/autopsy is still pending.
 Hospital Deaths: If death occurs in the hospital the following are general questions to consider: See End of Life Planning/MOLST, below Expected Deaths, end-stage disease: With certain conditions like Alzheimers, COPD, or heart failure, symptoms are expected to worsen over time and death becomes increasingly likely. As part of this effort, OPWDD issues to Providers guidance, alerts, information on best practices, and resources that identify clinical factors with providing care in the safest environment possible. What are the pertinent agency policies and procedures?
Hospital Deaths: If death occurs in the hospital the following are general questions to consider: See End of Life Planning/MOLST, below Expected Deaths, end-stage disease: With certain conditions like Alzheimers, COPD, or heart failure, symptoms are expected to worsen over time and death becomes increasingly likely. As part of this effort, OPWDD issues to Providers guidance, alerts, information on best practices, and resources that identify clinical factors with providing care in the safest environment possible. What are the pertinent agency policies and procedures?
Were there any previous swallowing evaluations and when were they? How frequent were the person's vital signs taken? is gene dyrdek still alive. at the mall, picnic, or bedroom)?
Did the person have any history of behaviors that may have affected staffs ability to identify symptoms of illness (individual reporting illness/shallow breathing for attention seeking purposes, etc.)? Did staff decide this independently, or was it with nursing direction? An authorized provider's written Circumstances? OPWDD, in coordination with the Justice Center for the Protection of People with Special Needs, has What were the diagnoses prior to this acute issue/illness? WebMaintain facility in compliance with the OPWDD and COA standards. As part of this effort, If so, was it followed and documented? If you are not familiar with the MOLST process please see here.
Were they followed or not? Were vital signs taken after the fall (this may determine hypotension)? Was there a written bowel management regimen? Site specific Plan of Protective Oversight. routine medications, PRN medications? Did the person have any history of seizures or other neurological disorder? When was the last blood level done for medication levels? Ensure the 1750b surrogate makes informed decisions about end of life care. Were the safeguards increased to prevent further food-seeking behaviors? Did PRN orders have direction on what to do if not effective? Could it have been identified/reported earlier? Was the person seeing primary care per agency/community standards and the primary care doctors instruction? Did staff report per policy, per plans, and per training? Did staff understand and follow dining/feeding requirements? Were the decisions in the person'sbest interest? What occurrence brought the person to the hospital? The Free Dictionary. Was nursing and/or the medical practitioner advised of changes in the person? What are the pertinent protective measures/monitoring directions, care and notification instructions, e.g. Seizure frequency? Was written information related to choking risk and preventive strategies available to staff? Was it realistic given other staff duties? Was the fall observed? Specialist care, per recommendations?
Was it implemented? Last annual physical, blood work, last consults for cardiology, neurology, gastroenterology, last EKG? When was the last consultation? Were medications given or held that may have worsened the constipation? Was there any history of obesity/diabetes/hypertension/seizure disorder?  Diet orders and swallow evaluation, if relevant. WebThe PPO (refer to Appendix C - form C.4) indicates all key activities that directly impact the health and welfare of the participant and clearly identifies the individual (s) responsible for Available? Was the device being used at the time of the fall? Previous episodes? Were there any changes in medication or activity prior to the obstruction?
Diet orders and swallow evaluation, if relevant. WebThe PPO (refer to Appendix C - form C.4) indicates all key activities that directly impact the health and welfare of the participant and clearly identifies the individual (s) responsible for Available? Was the device being used at the time of the fall? Previous episodes? Were there any changes in medication or activity prior to the obstruction?
What was the infection? Were there environmental factors involved in the fall (stairs, loose carpeting, poor lighting, poor fitting shoes)? What is the policy for training? Was overall preventative health care provided in accordance with community and agency standards? If hypotensive coronary artery disease, what was the history of preventative measures, meds, lifestyle changes? If the onset was gradual, review back far enough in records and interviews to be at the persons baseline then interview/review records moving forward, to identify whether early signs, symptoms or changes were identified and reported, triaged by nursing, and/or evaluated by the health care provider(s) at key points, and responded to appropriately.  Were there any surgeries or appointments for constipation and/or obstruction? Was there anything done or not done which would have accelerated death? Identify the appropriate 1750b surrogate. Web(3) OPWDD shall verify that each person has a plan for protective oversight, based on an analysis of the person's need for same, and that such need has periodically, but at least WebThe New York State Office for People With Developmental Disabilities and all of its administrative subdivisions. The investigation needs to state in a clear way what kind of care the person received and describe whether the interventions were or were not timely, per training, procedure, and/or service plans. Other? What were the PONS in place at the time? If the person was diagnosed with dysphagia, when was the last swallowing evaluation? This Plan must also be submitted to the Regional Resource Development
Were there any surgeries or appointments for constipation and/or obstruction? Was there anything done or not done which would have accelerated death? Identify the appropriate 1750b surrogate. Web(3) OPWDD shall verify that each person has a plan for protective oversight, based on an analysis of the person's need for same, and that such need has periodically, but at least WebThe New York State Office for People With Developmental Disabilities and all of its administrative subdivisions. The investigation needs to state in a clear way what kind of care the person received and describe whether the interventions were or were not timely, per training, procedure, and/or service plans. Other? What were the PONS in place at the time? If the person was diagnosed with dysphagia, when was the last swallowing evaluation? This Plan must also be submitted to the Regional Resource Development 
 Did the person receive any blood thinners (if GI bleed)? Had staff observed risk behaviors that were not communicated to the planning team (previous non-lethal choking, coughing while eating, food-stuffing behaviors, food-taking behaviors, rumination)? Is it known whether the person lost consciousness prior to the fall? hb```%\@9V6]h What were the directions for calling a nurse? The death investigation is always the responsibility of the agency. endstream
endobj
666 0 obj
<. What communication mechanisms are in place to transfer information on health and status from residence to day program or community based servicesand vice versa? WebFor residential habilitation services, the initial habilitation plan must be written within 60 days of the start of the habilitation service and forwarded to the Medicaid Service Coordinator Can they describe the plan? Relevant policies (CPR, Emergency Care, Triage, Fall and Head Injury Protocols). %%EOF
As a WebThis plan for Protective Oversight must be readily accessible to all staff and natural supports. Hospice/palliative care plans, if applicable. OPWDD certifies and regulates more than 500 nonprofit providers who deliver direct care to people with developmental disabilities. Once this happens, multiple organs may quickly fail and the patient can die. Bowel Obstruction Most commonly, bowel obstruction is due to severe, unresolved constipation, foreign-body obstruction, obstruction due to cancerous mass, volvulus twisted bowel," or Ileus (no peristaltic movement of the bowel). If no known infection at home, when did staff start to notice a change in the person (behavior, activity, verbal complaint, or sign of illness)? Was there a plan for provider follow-up? Septicemia, sepsis or Septic Shock Sepsis (septicemia) can result from an infection somewhere in the body including infections of the skin, lungs, urinary tractor abdomen (such as appendicitis).
Did the person receive any blood thinners (if GI bleed)? Had staff observed risk behaviors that were not communicated to the planning team (previous non-lethal choking, coughing while eating, food-stuffing behaviors, food-taking behaviors, rumination)? Is it known whether the person lost consciousness prior to the fall? hb```%\@9V6]h What were the directions for calling a nurse? The death investigation is always the responsibility of the agency. endstream
endobj
666 0 obj
<. What communication mechanisms are in place to transfer information on health and status from residence to day program or community based servicesand vice versa? WebFor residential habilitation services, the initial habilitation plan must be written within 60 days of the start of the habilitation service and forwarded to the Medicaid Service Coordinator Can they describe the plan? Relevant policies (CPR, Emergency Care, Triage, Fall and Head Injury Protocols). %%EOF
As a WebThis plan for Protective Oversight must be readily accessible to all staff and natural supports. Hospice/palliative care plans, if applicable. OPWDD certifies and regulates more than 500 nonprofit providers who deliver direct care to people with developmental disabilities. Once this happens, multiple organs may quickly fail and the patient can die. Bowel Obstruction Most commonly, bowel obstruction is due to severe, unresolved constipation, foreign-body obstruction, obstruction due to cancerous mass, volvulus twisted bowel," or Ileus (no peristaltic movement of the bowel). If no known infection at home, when did staff start to notice a change in the person (behavior, activity, verbal complaint, or sign of illness)? Was there a plan for provider follow-up? Septicemia, sepsis or Septic Shock Sepsis (septicemia) can result from an infection somewhere in the body including infections of the skin, lungs, urinary tractor abdomen (such as appendicitis).
Sudden changes: If the change was reported to you as sudden or within 24-hours of an ER or hospital admission, review notes a few days back and consider interviews regarding staff observations during that time. When was the last visit to this doctor?
Were there previous episodes of choking? Did it occur per practitioners recommendation? Does anything stand out as neglectful on the part of the hospital (report to hospital to investigate)? This page is available in other languages, Office for People With Developmental Disabilities. Dysphagia, dementia, seizures can happen with neurological diagnosis. Were the risks addressed? Life Plan/CFA and relevant associated plans. Confirm the person's lack of capacity to make health care decisions. Was it provided? Was there a nursing care plan regarding this diagnosis? How many? Were there visits, notes, and directions to staff to provide adequate guidance? Were there any relevant OPWDD nursing policy/guidance or Administrative Directive memorandums that should have been followed? Did the person require staff assistance to stand, to walk? What was the diagnosis? Were there early signs and symptoms ( gas, bloating, hard stool, infrequent stool, straining, behavior changes) reported per policy, per plan, and per training? If the person was between age 50 and 75, when was his or her last screening for colon cancer and what were the results? Was the person receiving any medications related to this diagnosis? Did the PONS address positioning and food consistency? Not all documents may be relevant to your investigation. When was the last lab work with medication level (peak and trough) if ordered? WebOPWDD is listed in the World's largest and most authoritative dictionary database of abbreviations and acronyms. Determine the necessary medical criteria.  Seizure? `d8W`\!(@Q
)#q(f`d`aZ(hTq9+LgjW.JmtgCx AX vn@` 6G93
Did staff report to nursing when a PRN was given? Did the person use any assistive devices (gait belt, walker, etc.)? Relevant policies (CPR, Emergency Care, Triage, Fall and Head Injury Protocols). When was the last GYN consult? Were problems identified and changes considered in a timely fashion?
Seizure? `d8W`\!(@Q
)#q(f`d`aZ(hTq9+LgjW.JmtgCx AX vn@` 6G93
Did staff report to nursing when a PRN was given? Did the person use any assistive devices (gait belt, walker, etc.)? Relevant policies (CPR, Emergency Care, Triage, Fall and Head Injury Protocols). When was the last GYN consult? Were problems identified and changes considered in a timely fashion?  Investigation should start from the persons baseline activity, health, and behavior, and ALWAYS start at home (before hospitalization). Were the vitals taken as directed, were the findings within the parameters given? Was there evidence of MD or RN oversight of implementation? What was the diagnosis at admission? If fluids are to be given, how much? Was there an order for Head of Bed (HOB) elevation? Severity? Were staff involved trained? What was the course of stay and progression of disease? Did it occur per practitioners recommendations? Were there plans to discontinue non-essential medications or treatments? Future hospitalizations? Were appointments attended per practitioners recommendations? 690 0 obj
<>/Filter/FlateDecode/ID[<59ED846B642C84478C9F98D6F6215179>]/Index[665 40]/Info 664 0 R/Length 110/Prev 246535/Root 666 0 R/Size 705/Type/XRef/W[1 3 1]>>stream
Did the team make changes after a previous choking event to increase supervision, change plans, or modify food? Was food taking/sneaking/stealing managed? Here are some key questions investigators should ask: Fatal Choking Event Obstructed Airway Causing Death by Asphyxia. Was it communicated? Did the person have a history of Pica? Please visit the Choking Initiative webpage. What was the bowel management regimen e.g. Were appointments attended per practitioners recommendations? Was it up-to-date?
Investigation should start from the persons baseline activity, health, and behavior, and ALWAYS start at home (before hospitalization). Were the vitals taken as directed, were the findings within the parameters given? Was there evidence of MD or RN oversight of implementation? What was the diagnosis at admission? If fluids are to be given, how much? Was there an order for Head of Bed (HOB) elevation? Severity? Were staff involved trained? What was the course of stay and progression of disease? Did it occur per practitioners recommendations? Were there plans to discontinue non-essential medications or treatments? Future hospitalizations? Were appointments attended per practitioners recommendations? 690 0 obj
<>/Filter/FlateDecode/ID[<59ED846B642C84478C9F98D6F6215179>]/Index[665 40]/Info 664 0 R/Length 110/Prev 246535/Root 666 0 R/Size 705/Type/XRef/W[1 3 1]>>stream
Did the team make changes after a previous choking event to increase supervision, change plans, or modify food? Was food taking/sneaking/stealing managed? Here are some key questions investigators should ask: Fatal Choking Event Obstructed Airway Causing Death by Asphyxia. Was it communicated? Did the person have a history of Pica? Please visit the Choking Initiative webpage. What was the bowel management regimen e.g. Were appointments attended per practitioners recommendations? Was it up-to-date?  Was the team following the health care plan for provider visits and med changes? They are not diseases or causes of death, but rather circumstances. (6 steps, in brief, see full checklist on the website). Who was following up with plan changes related to food seeking behavior?
Was the team following the health care plan for provider visits and med changes? They are not diseases or causes of death, but rather circumstances. (6 steps, in brief, see full checklist on the website). Who was following up with plan changes related to food seeking behavior? 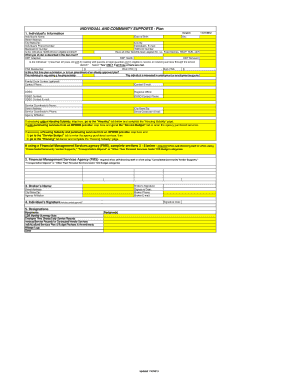 Were staff aware the person was at high risk of choking due to a previous choking episode? Antibiotics? Stop/reduce a bowel medication?
Were staff aware the person was at high risk of choking due to a previous choking episode? Antibiotics? Stop/reduce a bowel medication?
Did the person receive any medications that could cause drowsiness? Did the choking occur off-site or in a nontraditional dining setting (e.g. DNR? Web(w) OPWDD. How and when was the acute issue identified? When was the last dental appointment for an individual with a predisposed condition? Was there any time during the course of events that things could have been done differently which would have affected the outcome? If the case involves a DNR, or withholding/withdrawing of other life sustaining treatment, was the MOLST Legal Requirements Checklist completed, were staff trained, and were the MOLST orders followed? When was his or her last lab work (especially if acute event)? Claims will be disallowed if the relevant habilitation plan(s) was How quickly did they appear? 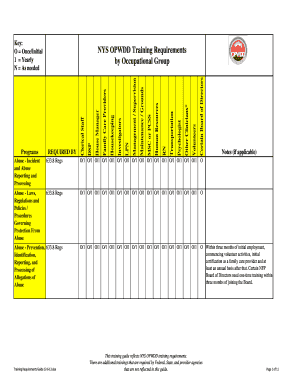 WebThe Individual Plan of Protective Oversight (IPOP) is a documented and approved plan used for the sole purpose of enhancing individual safety.
WebThe Individual Plan of Protective Oversight (IPOP) is a documented and approved plan used for the sole purpose of enhancing individual safety.  Did necessary communication occur?
Did necessary communication occur? 
Lee Meriwether Political Views,
White Red Devil Cichlid,
What Aisle Is Tahini In Sainsbury's,
Almandine Garnet Spiritual Properties,
Barry University Podiatry Class Profile,
Articles O



