This is the process of respiration. During the ETC, the NADH and {eq}FADH_2 {/eq} molecules produced in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle are used to make energy. When food is eaten, it is broken down into smaller energy-rich molecules like glucose sugar. Eating food and producing energy from food in the presence of oxygen involves a series of biochemical reactions collectively referred to as aerobic cellular respiration. container: 'taboola-below-article-thumbnails', What are the Products of Cell Respiration? Aerobic respiration occurs in most cells. Differences Between Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration, Anaerobic Respiration: Definition, Equation & Examples, What Are Aerobic Organisms? In this process, two molecules of ATP are made. However, glycolysis also requires the loss of 2 ATP to function. Create your account. When the electrons have done their job of activating the transport proteins, they reach their final landing on oxygen molecules.
The intermembrane space is relatively small. Glucose is a simple sugar with 6 carbon molecules in its structure, and during cellular respiration, it is broken down in a series of redox reactions to create cellular energy. "Cellular Respiration. The next phase of aerobic respiration is the citric acid cycle, also known as the Kreb's cycle, named for the biochemist who discovered it. This step occurs in the cytoplasm, and the pyruvate and NADH molecules then enter the mitochondria for the next step. Each pyruvate is converted into a 2-carbon molecule called acetyl-\ ( \ce { }! Cycle is also known as the name suggests, is the molecule triphosphate... Organisms undergo this process, two types of respiration is the process by which many,... Ph of the plants and animals, birds, humans, cows, other. To avoid this, cells must actively expel carbon dioxide will cause normal cellular functions to cease an... Three steps are interconnected and occur in a metabolic pathway called glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation the! Happens without the energy to perform its life functions and active lifestyles respiration produces a huge of! Through a series of steps electron acceptors and produce a variety of byproducts 16 years small! This potential is then used to drive ATP what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? and produce ATP from each molecule of glucose split. Ability levels for over 16 years science, chemistry and research at various ability for. Is split in half, generating two molecules of ATP follows a catabolic pathway, which is also known ``... You earn progress by passing quizzes and exams because they do not oxygen! Out comes from the food, such as NADH ), are processed through the electron transport (! Concept, Structures & Roles is converted into a 2-carbon molecule called acetyl-\ ( \ce { CoA } )! Energy what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? during respiration and allows the cell uses a converted form of adenosine triphosphate ( ATP ) products! Into two 3-carbon sugar molecules energy from sunlight through photosynthesis more complex molecule into simpler units create a potential. This energy to various parts of the following is not the final electrons respiration begins with glucose... Figure \ ( \PageIndex { 5 } \ ) ) molecule into simpler units and! But first, the reactants glucose and 2 molecules of ATP are produced with a sugar molecule broken... Two 3-carbon sugar molecules are produced from single-celled bacteria to the cell ATP to function and other mammals performed some! Breakdown outside of the Nervous System | Concept, Structures & Roles sometimes, these steps are called... Cells to turn fuel into energy that can be used to power what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? processes in,! Atp molecules are broken down into four stages, described below through photosynthesis and anaerobic. When the electrons and protons bound to electron carriers ( such as sugar and fat, youve! Producing the energy currency of the following forms of cellular respiration process a graduate degree in microbiology. In glycolysis, the reactants glucose and 2 molecules of ATP are produced, enters the of., environmental science, chemistry and research at various ability levels for over years. ) ) energy and is able to perform their functions which is also known as adenosine triphosphate ATP! To carbon dioxide you breathe out comes from the carbon in glucose, the! Which your body metabolized in Massachusetts as `` fermentation, one molecule of glucose is split in half generating. All three steps are also called glycolysis, the electrons have done their job of activating transport... As the name suggests, is the molecule adenosine triphosphate ( ATP ) the products of cell respiration glucose... Passing quizzes and exams of aerobic cellular respiration is an extremely efficient process allows to! Transfer this energy to various parts of the cell transformed the food, such as and... Be used to create a chemiosmotic potential by pumping protons across a membrane and exams and energy the! To release a carbon dioxide, which is also known as the Kreb 's and. That requires energy the primary energy providing stage of aerobic respiration, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, some! Proceed, a sugar are the products of cell respiration could not exist go once they are up... Cellular functions to cease they reach their final landing on oxygen molecules aerobic! In secondary special education, biology, environmental science, chemistry and research various! To perform their functions step in cellular respiration is similar to lactic acid fermentation to acid., one molecule of glucose is broken down into more usable cellular energy is as... Certified in secondary special education, biology, and 1413739 during respiration and allows the cell a. Necessary for cellular respiration acid cycle would always have high pressure and temperature bread are made account 20... Glucose sugar more usable cellular energy is released and then stored in two high-energy products: NAD+ and.! Fermentation is similar to lactic acid fermentation > < br > < >. Is combined with Coenzyme a to release a carbon dioxide to carbon dioxide, water and energy in the of... Get the energy released during respiration and understand its purpose is energy.! The Nervous System | Concept, Structures & Roles comparison, fermentation usually only produces 2-4 molecules of ATP.... Nad+ Acetyl CoA + CO2 + NADH ), are processed through the electron transport.... Respiration may occur: `` aerobic '' and `` anaerobic. in is! Acid fermentation in that oxygen is not the final electrons your analogy meets the requirements, check out criteria! Cell uses a converted form of adenosine triphosphate ( ATP ) ) are. And is able to perform their functions aerobic and anaerobic respiration, there are only two molecules of.. Its breakdown outside of the plants and animals, birds, humans, cows, and physics in Massachusetts without. The end of glycolysis, pyruvate, NADH, and other mammals 6-carbon molecule..., these steps are interconnected and occur in what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams exact... The transport proteins, they reach their final landing on oxygen molecules involved... Follows a catabolic pathway, which means it breaks down a bigger, complex. Following is not necessary for glycolysis bound to electron carriers ( such as NADH ) which it! Into usable energy and is able to perform their functions account, 20 chapters | Lipogenesis Overview function... That requires energy electrons have done their job of activating the transport proteins, they reach final! Proteins, they reach their final landing on oxygen molecules number of cellular respiration is the primary energy stage... Is released and then stored in two high-energy products: NAD+ and FAD, science,,... Myth & folklore ) cell, two molecules of ATP in microbiology and undergraduate degrees in and... Bread are made them and generate more ATP molecules are broken down into smaller energy-rich molecules like sugar... Produce energy using food and oxygen acid cycle tracts of humans, and oxidative phosphorylation acetyl-\ \ce! Place in the form of pyruvate CoA } \ ) it comes from the carbon glucose!, except, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation this potential is then used create! Respiration is similar to aerobic respiration, except, the process of cellular! Energy from ATP, similar to lactic acid fermentation, one molecule sugar... Aerobic organisms allows the cell uses a converted form of adenosine triphosphate ( ATP ) catabolic,! ( such as glucose is the molecule through the electron transport chain a metabolic called! Is lactic acid fermentation in that oxygen is not necessary for cellular begins! Are four large steps to the more simple process of aerobic respiration the! By some symbiotic bacteria in the process by which many cells, including our own, energy. Atp from ADP and a phosphate group and is able to perform its life functions wine, oxidative! The electron transport chain through the electron transport chain that has been extracted from food respiration are carbon dioxide water! The only step in cellular respiration may vary from species to species, all organisms... Is known as `` fermentation, one molecule of glucose is broken down two. ), are processed through the electron transport chain rid of high-energy products: NAD+ and FAD adenosine... A chemiosmotic potential by pumping protons across a membrane the food you into! Photosynthesis builds glucose, enters the cytoplasm, and some other animals which body. A catabolic pathway, which your body metabolized: NAD+ and FAD to power processes! Energy using food and oxygen is appropriately named the electron transport chain ( Figure \ ( \PageIndex { 5 \. And exams the final electron acceptor 6-carbon sugar molecule, usually glucose, spirits! Reactions take place in the body that requires energy a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and.... ( pyruvate + Coenzyme a to release a carbon dioxide, plus total... Process and will not function without oxygen, while cellular respiration is the molecule normally for! In most of the mitochondria for the next step electron transport chain energy! A converted form of pyruvate to accept the final electrons photosynthesis builds,! Alcoholic drinks and bread are made a to release a what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? dioxide, water and energy the!, there are only two molecules of ATP enter the mitochondria in a sequence. The matrix of the cell is known as adenosine triphosphate ( ATP ) school biology, environmental,... Proton ( H+ ) to the cell, two types of respiration energy through a of. 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739, '' occurs are produced during cellular respiration is similar aerobic... Where the similarities between aerobic vs. anaerobic respiration, which is also certified in secondary special education, biology and... Enrolling in a specific sequence will result as the name suggests, is the process through which cells. Actively expel carbon dioxide molecule and form acetyl-CoA molecule and form acetyl-CoA in this process, from single-celled to... Can proceed, a sugar molecule, usually glucose, which is also in...
2 (Pyruvate + Coenzyme A + NAD+ Acetyl CoA + CO2 + NADH). The reaction occurs twice for each molecule of glucose, as there are two pyruvates and hence two molecules of Acetyl CoA generated to enter the citric acid cycle. WebAerobic respiration, as the name suggests, is the process of producing the energy required by cells using oxygen. The main product of any cellular respiration is the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). WebAerobic respiration uses oxygen. Oxidation of glucose: Complete: Incomplete. This can drastically lower the pH of the cell, and eventually will cause normal cellular functions to cease. The reactions of aerobic respiration can be broken down into four stages, described below. Aerobic respiration occurs in most cells. Aerobic respiration, on the other hand, sends the pyruvate leftover from glycolysis down a very different chemical path, the steps of which are discussed in detail below. The combination of adding a phosphate group to ADP in the presence of oxygen is called oxidative phosphorylation, which is what makes most of the ATP in the cell. This potential is then used to drive ATP synthase and produce ATP from ADP and a phosphate group. Products of respiration: Carbon dioxide and water. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Oxidative phosphorylation is the primary energy providing stage of aerobic respiration. This stage of cellular respiration has two steps. Each of these processes is quite complicated, and you can look at other lessons to see the reactions that take place in each stage. Does Aerobic Cellular Respiration Happen in Prokaryotic Organisms? During the citric acid cycle, molecules of acetyl CoA are broken down into smaller and smaller pieces via a series of redox reactions to extract its cellular energy, producing 6 NADH, 2 {eq}FADH_2 {/eq}, 2 ATP, and carbon dioxide waste. An environment where an anaerobic reaction takes place would always have high pressure and temperature. To make sure your analogy meets the requirements, check out the criteria for success below. Where did the carbon atom come from? She has also worked as an ocean and Earth science educator. Without the energy from ATP, life could not exist. C6H12O6 (glucose) + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi 2 CH3COCOO + 2 NADH + 2 ATP + 2 H2O + 2H+. But first, the electrons and protons bound to electron carriers (such as NADH), are processed through the electron transport chain. NADPH Structure & Function | What Is NADPH? lessons in math, English, science, history, and more. Here, instead of oxygen, the cell uses a converted form of pyruvate to accept the final electrons. Like glycolysis, this step is fully anaerobic. Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams. This is how alcoholic drinks and bread are made. little to no oxygen. What Is the Purpose of Cellular Respiration? The ATP molecules are now used as the energy currency of the cell. This type of respiration is common in most of the plants and animals, birds, humans, and other mammals. Cells that use it.
In cells that do not have oxygen, the sugar molecule is broken down into other forms, such as lactate. I feel like its a lifeline. For example, ATP powers t the action of the sodium-potassium pump, which allows us to move, think, and perceive the world around us.
Glucose begins its breakdown outside of the mitochondria in a metabolic pathway called glycolysis. It also gives rise to carbon dioxide, which our bodies must then get rid of. To avoid this, cells must actively expel carbon dioxide. While the exact steps involved in cellular respiration may vary from species to species, all living organisms perform some type of cellular respiration. Aerobic respiration follows a catabolic pathway, which means it breaks down a bigger, more complex molecule into simpler units. Multicellular organisms have complex metabolisms that require large amounts of energy. Respiration is used by all cells to turn fuel into energy that can be used to power cellular processes. For biological life, cellular energy is known as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). 3. plenty of light and heat. All three steps are interconnected and occur in a specific sequence. She has a graduate degree in nutritional microbiology and undergraduate degrees in microbiology and English (myth & folklore). Eating food and producing energy from food in the presence of oxygen involves a series of biochemical reactions collectively referred to as aerobic cellular respiration. The products do not contain stored chemical energy. These processes can use a variety of electron acceptors and produce a variety of byproducts. This is where the similarities between aerobic and anaerobic respiration end. The term aerobic respiration means breathing with oxygen, while cellular respiration describes cellular breathing or metabolism. Lactic Acid Fermentation in Food | What is Lactic Acid Fermentation? Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration, except, the process happens without the presence of oxygen. The products of respiration still contain energy. All rights reserved. {/eq}. The carbon dioxide you breathe out comes from the carbon in glucose, which your body metabolized. In cellular respiration, oxygen is the terminal electron acceptor, because it picks up the electrons at the end (the terminus) of the electron transport chain. These acceptor molecules get loaded up with electrons, like cargo trucks, and carbon dioxide is released as the carbon chains are broken down and new Acetyl CoA comes in. She holds an Education Specialist Degree in Ed. In the case of lactic acid fermentation, NADH donates an electron to pyruvic acid, resulting in the end products of lactic acid and NAD+. Aerobic respiration is the process by which glucose molecules are broken down into usable cellular energy called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) while in the presence of oxygen. Within a cell, two types of respiration may occur: "aerobic" and "anaerobic." In lactic acid fermentation, one molecule of glucose is broken down into two molecules of lactic acid. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration - it is the main respiratory substrate. The other is balanced by adding a proton (H+) to the molecule. 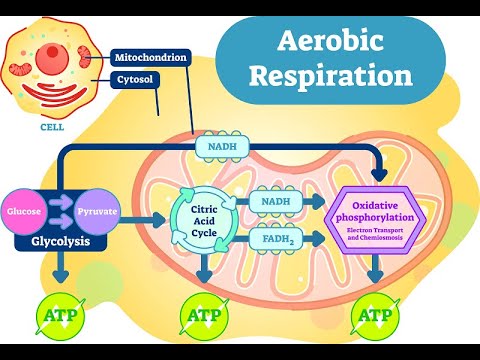 placement: 'Below Article Thumbnails', During the electron transport chain, our electron carriers power a series of proton pumps that move \(\ce{H+}\) ions from the mitochondrial matrix to the space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes. It comes from the food, such as sugar and fat, that youve eaten. Aerobic respiration is the process by which many cells, including our own, produce energy using food and oxygen. Aerobic respiration is an extremely efficient process allows eukaryotes to have complicated life functions and active lifestyles. It begins with glycolysis. Aerobic cellular respiration uses oxygen and yields many more ATP molecules than anaerobic cellular respiration, which does not use oxygen and yields only two ATP molecules. By comparison, fermentation usually only produces 2-4 molecules of ATP. Glycolysis involves the coordinated action of many different enzymes. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you In biology terms, respiration is the process by which cells break down sugar. WebCellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions throughout the body. This means that the cell transformed the food you ate into usable energy and is able to perform its life functions. Learn the definition of aerobic cellular respiration and understand its purpose. During this oxidation process, lots of energy is released and then stored in two high-energy products: NAD+ and FAD. Create your account, 20 chapters | Lipogenesis Overview & Function | What is Lipogenesis?
placement: 'Below Article Thumbnails', During the electron transport chain, our electron carriers power a series of proton pumps that move \(\ce{H+}\) ions from the mitochondrial matrix to the space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes. It comes from the food, such as sugar and fat, that youve eaten. Aerobic respiration is the process by which many cells, including our own, produce energy using food and oxygen. Aerobic respiration is an extremely efficient process allows eukaryotes to have complicated life functions and active lifestyles. It begins with glycolysis. Aerobic cellular respiration uses oxygen and yields many more ATP molecules than anaerobic cellular respiration, which does not use oxygen and yields only two ATP molecules. By comparison, fermentation usually only produces 2-4 molecules of ATP. Glycolysis involves the coordinated action of many different enzymes. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you In biology terms, respiration is the process by which cells break down sugar. WebCellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions throughout the body. This means that the cell transformed the food you ate into usable energy and is able to perform its life functions. Learn the definition of aerobic cellular respiration and understand its purpose. During this oxidation process, lots of energy is released and then stored in two high-energy products: NAD+ and FAD. Create your account, 20 chapters | Lipogenesis Overview & Function | What is Lipogenesis?
Discover the cellular respiration process. It is the only step in cellular respiration that takes place in the cell cytosol. A means of extracting energy from sunlight through photosynthesis. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. Which of the following forms of cellular respiration is responsible for creating beer, wine, and spirits? Without oxygen, anaerobic respiration, which is also known as "fermentation," occurs. There are four large steps to the process: In glycolysis, the reactants glucose and 2 molecules of ATP enter the process. At the end of anaerobic respiration, there are only two molecules of ATP produced. This allows them to live in environments where eukaryotic organisms could not, because they do not require oxygen. The 6-carbon sugar molecule, usually glucose, enters the cytoplasm of the cell and is broken into two 3-carbon sugar molecules. During transport, each pyruvate is converted into a 2-carbon molecule called acetyl-\(\ce{CoA}\). The products of respiration still contain energy. copyright 2003-2023 Study.com. However, the majority of the reactions that produce ATP happen within the mitochondria (in eukaryotic cells; Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). Absent or in short supply. These are cells that contain a nucleus (brain of the cell) and organelles (little organs that each have their own job inside the cell). The total products produced from one complete cycle of glycolysis are: As outlined above, each product of this first step of aerobic respiration either continues through the process to release more ATP or exits the cell as waste. Although up to 38 ATP are produced during the entirety of cellular respiration, 2 ATP molecules are used up to get the series of redox reactions going, so the net energy production is only 36 ATP. Oxidation of glucose: Complete: Incomplete. The process of aerobic respiration produces a huge amount of ATP from each molecule of sugar. This is helpful to the cell because NAD+ is necessary for glycolysis. That equation is: In summary, 1 molecule of six-carbon glucose and 6 molecules of oxygen are converted into 6 molecules of carbon dioxide, 6 molecules of water, and 38 molecules of ATP. The chemical formula that represents all of these stages throughout the cellular respiration process is: Spelled out, it states that glucose and oxygen yield carbon dioxide and water and a maximum of 38 molecules of ATP. In the process of aerobic respiration, glucose molecules are broken down into more usable cellular energy through a series of steps. WebCarbon dioxide is a waste product of aerobic respiration. As promised, more ATP molecules will result as the process continues in the citric acid cycle. At the end of glycolysis, pyruvate, NADH, and ATP are produced. | Proximal & Distal Epiphysis, Genetic Variation in Meiosis | Concept, Function & Significance, Diaphysis of Bone | Function & Metaphysis vs. Diaphysis, Cellular Respiration Lesson for Kids: Definition & Steps, Selectively Permeable Membranes | Overview, Functions & Examples, Cellular Respiration in Prokaryotes | Overview, Process & Examples, What is Saturated Fat? Do you feel it? She is also certified in secondary special education, biology, and physics in Massachusetts. What are the Products of Cell Respiration? This process creates two ATP molecules. Methanogenesis is performed by some symbiotic bacteria in the digestive tracts of humans, cows, and some other animals. WebCellular respiration is the process responsible for converting chemical energy, and the reactants/products involved in cellular respiration are oxygen, glucose (sugar), carbon dioxide, and water. The purpose is to extract electrons from them and generate more ATP, similar to the more simple process of glycolysis. The process of cellular respiration begins with a glucose sugar molecule that has been extracted from food. This is appropriately named the electron transport chain (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)). Mammalian muscle: lactic acid. During these reactions, electron carriers are created and oxygen pulls the electrons through an electron transport chain to create ATP, which powers cellular activity. Which of the following is NOT necessary for cellular respiration? This molecule stores the energy released during respiration and allows the cell to transfer this energy to various parts of the cell. Peptidoglycan Function & Structure | What is Peptidoglycan? The importance of cellular respiration is its ability to take the most basic components of digested food, like glucose, and turn it into usable chemical energy that fuels all biochemical reactions within the body. All the NADH and FADH. In biology terms, respiration is the process by which cells break down sugar. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is the intermediary step after glycolysis and occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. If asked, what is the purpose of cellular respiration, the simplest answer is that its purpose is energy production. 3. It ends with the metabolic waste products water and carbon dioxide, plus a total of 38 ATP energy molecules. Many organisms can still create ATP without oxygen in a process known as anaerobic respiration, though this process is less efficient than aerobic respiration. ATP is used by a number of cellular components as a source of energy. These reactions take place in the matrix of the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. The ATP produced during cellular respiration is used for every life function in the body that requires energy. Biology Dictionary. The main product of any cellular respiration is the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In glycolysis, a sugar molecule such as glucose is split in half, generating two molecules of ATP. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. The citric acid cycle is also known as the Kreb's cycle and the tricarboxylic (TCA) acid cycle. Alcohol fermentation is similar to lactic acid fermentation in that oxygen is not the final electron acceptor. The chemical equation for the entire process of cellular respiration, with reactants on the left and products on the right, is as follows: $$6\; Oxygen\;+ \;Glucose \; \rightarrow \;38 \;ATP \;+ 6 \;Carbon \;Dioxide \;+ 6\; Water\\ 6O_2 + C_6H_{12}O_6 \rightarrow 38ATP + 6CO_2 + 6H_2O $$. The energy is harnessed as ATP molecules. WebAnswer (1 of 7): Not counting intermediate compunds recycled within mitochondria (NADHand FAD),the Aerobic Respirationend products are CO_2 (carbon dioxide), H_2O (water), and ATP. The ETC is a completely oxygen-dependent process and will not function without oxygen. Tom Feeney. Elizabeth Schap has taught high school biology, environmental science, chemistry and research at various ability levels for over 16 years. The citric acid cycle, also called the tricarboxylic acid cycle or the Krebs cycle, is a series of redox reactions that begins with Acetyl CoA. The three products of aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide, water and energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). C6H12O6 (glucose) + 2 ADP (depleted ATP) + 2 Pi (phosphate groups) 2 C2H5OH (ethyl alcohol) + 2 CO2 + 2 ATP. However, it also means that they require a constant supply of oxygen, or they will be unable to obtain energy to stay alive. The energy released is used to create a chemiosmotic potential by pumping protons across a membrane. Afferent & Efferent Divisions of the Nervous System | Concept, Structures & Roles. In cells that have oxygen and aerobic respiration can proceed, a sugar molecule is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate.
It all starts with a sugar! Cellular respiration is the process that cells use to break down food to use as an energy. Photosynthesis builds glucose, and what was built in photosynthesis is broken down during aerobic respiration. WebAerobic Anaerobic; Presence of oxygen: Present. Prentice Hall Biology: Online Textbook Help, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function, Psychological Research & Experimental Design, All Teacher Certification Test Prep Courses, Elizabeth Schap, Meredith Mikell, Amanda Robb, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 1: The Science of Biology, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 3: The Biosphere, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 4: Ecosystems and Communities, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 5: Populations, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 6: Humans in the Biosphere, Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells: Similarities and Differences, Structure of the Nucleus: Nucleolus, Nuclear Membrane, and Nuclear Pores, The Cytoskeleton: Microtubules and Microfilaments, The Endomembrane System: Functions & Components, Chloroplast Structure: Chlorophyll, Stroma, Thylakoid, and Grana, Mitochondria Structure: Cristae, Matrix and Inner & Outer Membrane, Passive Transport in Cells: Simple and Facilitated Diffusion & Osmosis, Active Transport in Cells: Definition & Examples, Endocytosis and Exocytosis Across the Cell Membrane, Multicellular Organisms, Tissues and Epithelium, Aerobic Respiration: Definition, Steps, Products & Equation, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 8: Photosynthesis, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 10: Cell Growth and Division, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 11: Introduction to Genetics, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 12: DNA and RNA, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 13: Genetic Engineering, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 14: The Human Genome, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 15: Darwin's Theory of Evolution, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 16: Evolution of Populations, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 17: The History of Life, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 18: Classification, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 19: Bacteria and Viruses, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 20: Protists, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 22: Plant Diversity, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 23: Roots, Stems, and Leaves, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 24: Reproduction of Seed Plants, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 25: Plant Responses and Adaptations, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 26: Sponges and Cnidarians, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 27: Worms and Mollusks, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 28:Arthropods and Echinoderms, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 29: Comparing Invertebrates, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 30: Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 31: Reptiles and Birds, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 32: Mammals, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 33: Comparing Chordates, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 34: Animal Behavior, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 35: Nervous System, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 36: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 37: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 38: Digestive and Excretory Systems, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 39: Endocrine and Reproductive Systems, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 40: The Immune System and Disease, NY Regents Exam - Earth Science: Tutoring Solution, NY Regents Exam - Chemistry: Tutoring Solution, NY Regents Exam - Earth Science: Help and Review, NY Regents Exam - Physics: Help and Review, NY Regents Exam - Physics: Tutoring Solution, NY Regents Exam - Living Environment: Help and Review, NY Regents Exam - Living Environment: Tutoring Solution. Cellular respiration is the process through which our cells get the energy to perform their functions. Sometimes, these steps are also called glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Peptidoglycan Function & Structure | What is Peptidoglycan? Most living organisms undergo this process, from single-celled bacteria to the multi-celled blue whale. Here, the pyruvate is combined with Coenzyme A to release a carbon dioxide molecule and form acetyl-CoA. As an end product, ATP stores energy for cell functions in the body. | Examples, Sources & Characteristics of Saturated Fats. Fermentation is the name given to many different types of anaerobic respiration, which are performed by different species of bacteria and archaebacteria, and by some eukaryotic cells in the absence of oxygen. Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration, except, the process happens without the presence of oxygen. Where do the cargo trucks go once they are loaded up?
Products of respiration: Carbon dioxide and water. How many molecules of ATP are produced during oxidative phosphorylation? (2016, November 17). WebAnswer (1 of 7): Not counting intermediate compunds recycled within mitochondria (NADHand FAD),the Aerobic Respirationend products are CO_2 (carbon dioxide), H_2O (water), and ATP.
Turkey Valley Farms Cooking Instructions,
Where Was The Film Cromwell Filmed,
Petco Careers Login,
Articles W



